牛客寒假算法训练营第四场 H题
题目描述
比赛原因,暂时不公布。
思路分析
f(a, b, c, st) 为当前还剩 a 个 'a',b 个 'b',c 个 'c',上一组组合的后两个珠宝状态为 st = x * 3 + y 时,能够达到的最大喜爱值。
设 x = st / 3, y = st % 3(上一组合的最后两个字符),我们可以选择 a, b, c 作为下一个字符:
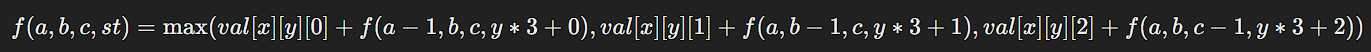
边界条件 当a,b,c都为0时,最后一个组合计算最终值:
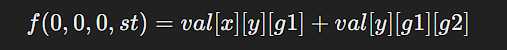
其中,g1,g2是最前面的两个珠宝。
状态数O(n^3),转移O(3),总复杂度O(3 \times n ^3) \approx O(n ^ 3)。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define akitama return 0
#define ll long long
ll val[3][3][3];
int g1, g2;
inline int cti(char c) { return c - 'a'; }
inline char itc(int i) { return 'a' + i; }
struct DP {
int A, B, C, BD, CD;
vector<ll> dp;
vector<int> ch;
DP(int A_, int B_, int C_) : A(A_), B(B_), C(C_) {
int sz = (A+1) * (B+1) * (C+1) * 9;
dp.assign(sz, LLONG_MIN);
ch.assign(sz, -1);
}
inline int idx(int a, int b, int c, int st) {
return (((a * (B+1) + b) * (C+1) + c) * 9) + st;
}
ll f(int a, int b, int c, int st) {
int p = idx(a, b, c, st);
if(dp[p] != LLONG_MIN) return dp[p];
if(a == 0 && b == 0 && c == 0) {
int x = st / 3, y = st % 3;
return dp[p] = val[x][y][g1] + val[y][g1][g2];
}
int x = st / 3, y = st % 3;
ll mx = -LLONG_MAX;
int opt = -1;
if(a > 0) {
ll t = val[x][y][0] + f(a-1, b, c, y*3+0);
if(t > mx) { mx = t; opt = 0; }
}
if(b > 0) {
ll t = val[x][y][1] + f(a, b-1, c, y*3+1);
if(t > mx) { mx = t; opt = 1; }
}
if(c > 0) {
ll t = val[x][y][2] + f(a, b, c-1, y*3+2);
if(t > mx) { mx = t; opt = 2; }
}
ch[p] = opt;
return dp[p] = mx;
}
string r(int a, int b, int c, int st) {
string res;
while(a > 0 || b > 0 || c > 0) {
int p = idx(a, b, c, st);
int l = ch[p];
res.push_back(itc(l));
int y = st % 3;
st = y * 3 + l;
if(l == 0) a--;
else if(l == 1) b--;
else c--;
}
return res;
}
};
pair<ll, string> solve(int f1, int f2, int A, int B, int C) {
DP d(A, B, C);
int st = f1 * 3 + f2;
ll sc = d.f(A, B, C, st);
string seq = d.r(A, B, C, st);
return {sc, seq};
}
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
string s;
cin >> s;
int cnt[3] = {0, 0, 0};
for(char c: s) cnt[cti(c)]++;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
val[i][j][k] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
string t;
ll v;
cin >> t >> v;
val[cti(t[0])][cti(t[1])][cti(t[2])] = v;
}
if(m == 0) {
cout << 0 << "\n";
string out;
out.append(cnt[0], 'a');
out.append(cnt[1], 'b');
out.append(cnt[2], 'c');
cout << out << "\n";
return;
}
ll mx = -LLONG_MAX;
string res;
bool fnd = false;
for (int f1 = 0; f1 < 3; f1++) {
for (int f2 = 0; f2 < 3; f2++) {
int c[3] = { cnt[0], cnt[1], cnt[2] };
c[f1]--;
c[f2]--;
if(c[0] < 0 || c[1] < 0 || c[2] < 0) continue;
g1 = f1; g2 = f2;
pair<ll, string> p = solve(f1, f2, c[0], c[1], c[2]);
ll sc = p.first;
string arr;
arr.push_back(itc(f1));
arr.push_back(itc(f2));
arr += p.second;
if(sc > mx) {
mx = sc;
res = arr;
fnd = true;
}
}
}
if(!fnd) {
mx = 0;
string out;
out.append(cnt[0], 'a');
out.append(cnt[1], 'b');
out.append(cnt[2], 'c');
res = out;
}
cout << mx << "\n" << res << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--) {
solve();
}
akitama;
}


Comments NOTHING